Search This Supplers Products:Lithium BatterySodium BatterySodium Battery CellHome BatterySolar GeneratorRv Battery&Marine Battery
Sodium Ion Battery VS Lithium Ion Battery:How To Choose?
sourceGoogle
publisherKayla He
time2023/11/29

- Sodium-ion batteries and lithium-ion batteries are two currently popular secondary battery technologies. They have some differences in terms of energy density, cost, safety, and application fields.
Sodium-ion batteries and lithium-ion batteries are two currently popular secondary battery technologies. They have some differences in terms of energy density, cost, safety, and application fields.Now, let's explore them together.
In the expanding realm of battery technology, the rivalry between sodium-ion (Na-ion) and lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries has taken center stage. As global demands for sustainable and efficient energy solutions escalate, a nuanced comprehension of these two technologies becomes imperative. In the subsequent exploration, we delve more profoundly into the distinctions, advantages, and challenges inherent in sodium-ion batteries when juxtaposed with the well-established lithium-ion battery.
Sodium Ion Battery VS Lithium Ion Battery
Characteristics of sodium-ion and lithium-ion batteries
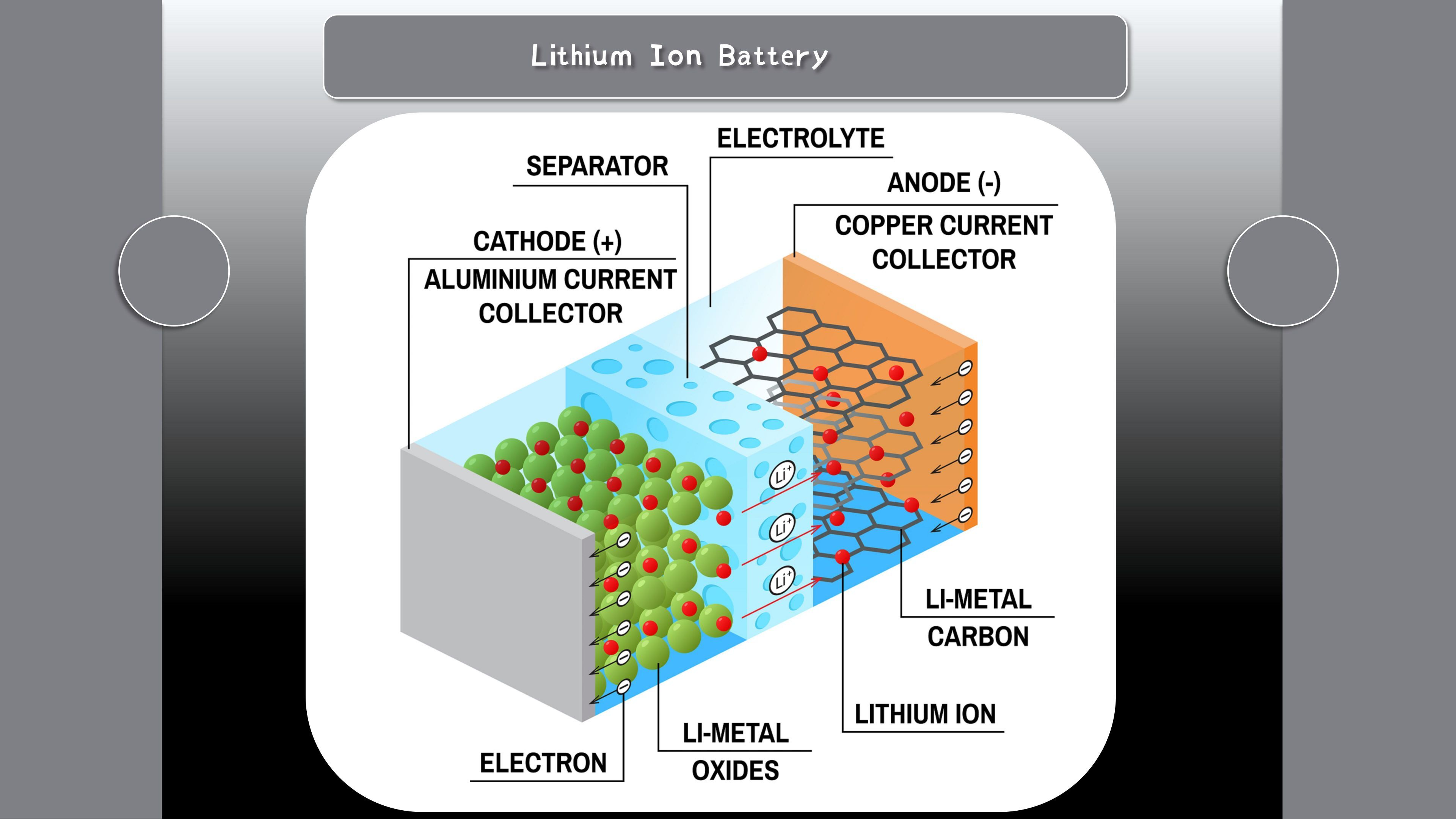
Sodium-ion batteries and lithium-ion batteries are two types of rechargeable batteries. Rechargeable batteries come in various types, with sodium-ion batteries and lithium-ion batteries standing out among them. The primary distinction lies in their composition and the materials employed in their electrodes. Sodium-ion batteries, categorized as secondary rechargeable batteries, utilize sodium as the negative electrode material and diverse positive electrode materials like carbon or oxide. Conversely, lithium-ion batteries, also classified as secondary rechargeable batteries, employ lithium as the negative electrode material, paired with various positive electrode materials such as lithium iron phosphate or lithium cobalt oxide.
Advantages of Sodium Ion Batteries

1. Rich in sodium resources
Sodium resource reserves are very abundant,it is one of the most abundant metallic elements on Earth, with much more reserves than lithium and more widespread distribution.The amount of sodium resources on the earth is more than 400 times that of lithium, and sodium resources are relatively evenly distributed around the world, while more than 80% of lithium resources are concentrated in the Americas and Australia. Therefore, in large-scale application scenarios, sodium batteries have no obvious resource constraints.
2. Lower cost
Sodium resources are much more abundant than lithium resources. Therefore,using sodium as the negative electrode material can reduce raw material costs. since sodium-ion batteries do not need to use expensive separators and copper foil, but can use cheaper polymer separators and aluminum foil, assembly costs can be reduced. According to calculations, when large-scale production of more than 100GWh is achieved, the direct material cost of each 1GWh of sodium-ion batteries produced will be 30% lower than the material cost of lithium batteries.
3.Higher safety
Since the internal resistance of sodium-ion batteries is higher than that of lithium batteries, they generate less instantaneous heat in the event of a short circuit, have lower temperature rises, and have higher thermal runaway temperatures than lithium batteries, and are safer. .Moreover, sodium batteries can operate normally in the temperature range of -40°C to 80°C, with a capacity retention rate of close to 90% in an environment of -20°C, and their high and low temperature performance is better than other secondary batteries.
4.Good low-temperature performance
The discharge retention rate of sodium-ion batteries in low-temperature environments is much higher than that of lithium-ion batteries. This is because the liquid electrolyte used in sodium-ion batteries is generally a mixture of organic solvents and inorganic salts, and its freezing point is much lower than the mixture of organic solvents and organic salts used in lithium-ion batteries. Hence, in severely cold conditions around minus 20 ℃, sodium-ion batteries demonstrate discharge retention rate of over 90%.
Advantages of Lithium Ion Batteries
1.Higher energy density
The high energy density of lithium batteries allows the battery unit to store more energy in a limited volume. Compared with sodium-ion batteries, lithium batteries can store more energy in the same size. This also means that devices using lithium batteries can have longer battery life, whether they are energy storage or electric vehicles.
2.Long life
Lithium batteries have a long service life, and sodium batteries are generally between 1000-4000 times. In comparison, lithium battery cycle life is between 3,000-10,000 times, and compared with sodium-ion batteries, lithium batteries can withstand more charge and discharge cycles
3.Higher power output
Lithium batteries not only have high energy density, they also have high power density.possess the ability to deliver substantial current output swiftly. This characteristic renders them particularly well-suited for devices demanding robust power performance, including power tools, electric motorcycles, and EVs.
4.Faster charging
Lithium-ion batteries generally boast faster charging capabilities when compared to their sodium-ion counterparts. This rapid charging ability constitutes a notable advantage, particularly in scenarios demanding swift recharging, such as in electric vehicles and portable electronic devices.
Different application scenarios of lithium batteries and sodium batteries
Features of Sodium Ion Battery
It can be seen by comparing the advantages and disadvantages of sodium-ion batteries and lithium-ion batteries. Obviously, for fields such as electric vehicles or Electric motorcycle that require high energy density and cruising range, the disadvantage of low energy density is the main shortcoming of sodium-ion batteries as power batteries. Energy density limitations also determine that it is difficult to form a strictly disruptive substitution between sodium-ion batteries and lithium-ion batteries. However, in areas with relatively low energy density requirements and in low-temperature environments, sodium-ion batteries are a better choice, such as in low-speed electric vehicles, electric bicycles, electric scooters, golf carts, energy storage equipment and other application scenarios.
Conclusion on Lithium and Sodium Batteries
In both energy storage and electric vehicle applications, sodium batteries and lithium batteries exhibit distinct sets of strengths and weaknesses. Selecting the appropriate battery involves a comprehensive evaluation of individual travel requirements, electric vehicle performance, and pricing considerations. At the current stage, a complete replacement of lithium batteries with sodium-ion batteries is challenging due to their complementary roles in different application fields. Sodium-ion batteries are more likely to serve as potential substitutes for lithium-ion batteries and complement them in specific contexts.
Welcome To Our Discussion Group For E-lary Battery.
Be respectful, be constructive, stay on topic, support other commenters, and report bad behavior.
For more insights on sodium-ion batteries, please leave a comment